A Template Strand Of Dna Contains The Nucleotide Sequence
A Template Strand Of Dna Contains The Nucleotide Sequence - Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding. A nucleotide has three parts:. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. Web recall that dna polymerases incorporate nucleotides (dntps) into a growing strand of dna, based on the. Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,. Web a template strand of dna contains the nucleotide sequence.
A nucleotide has three parts:. Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,. Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. Web recall that dna polymerases incorporate nucleotides (dntps) into a growing strand of dna, based on the. Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding. Web a template strand of dna contains the nucleotide sequence.
Web recall that dna polymerases incorporate nucleotides (dntps) into a growing strand of dna, based on the. Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. Web a template strand of dna contains the nucleotide sequence. Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. A nucleotide has three parts:. Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,.
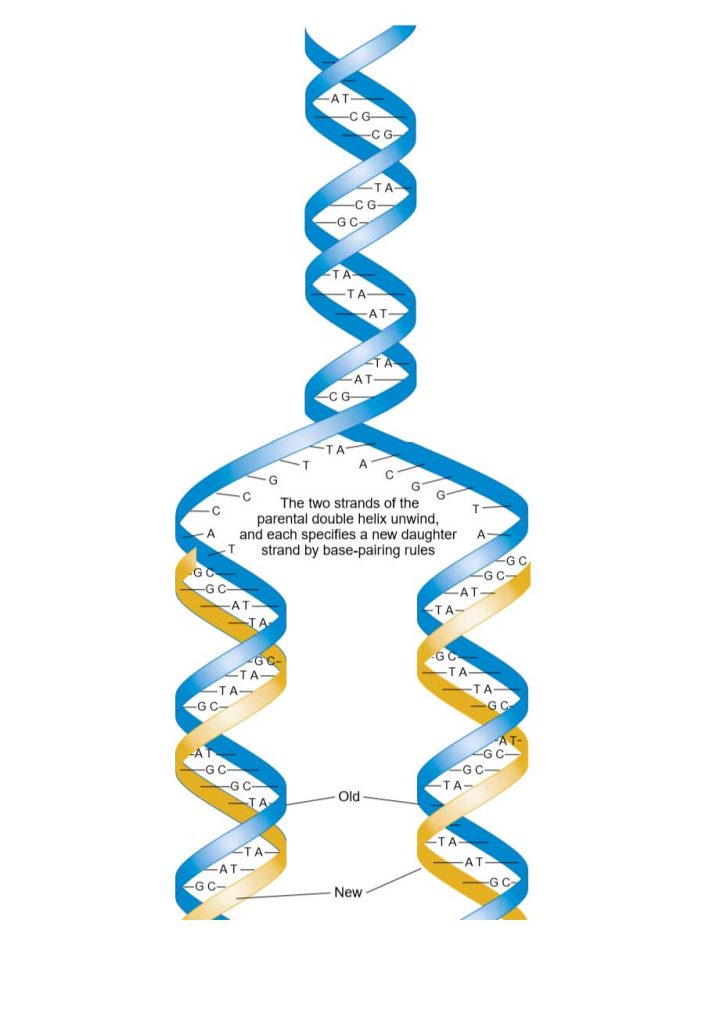
In semiconservative DNA replication an existing DNA molecule separates
A nucleotide has three parts:. Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding. Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,..
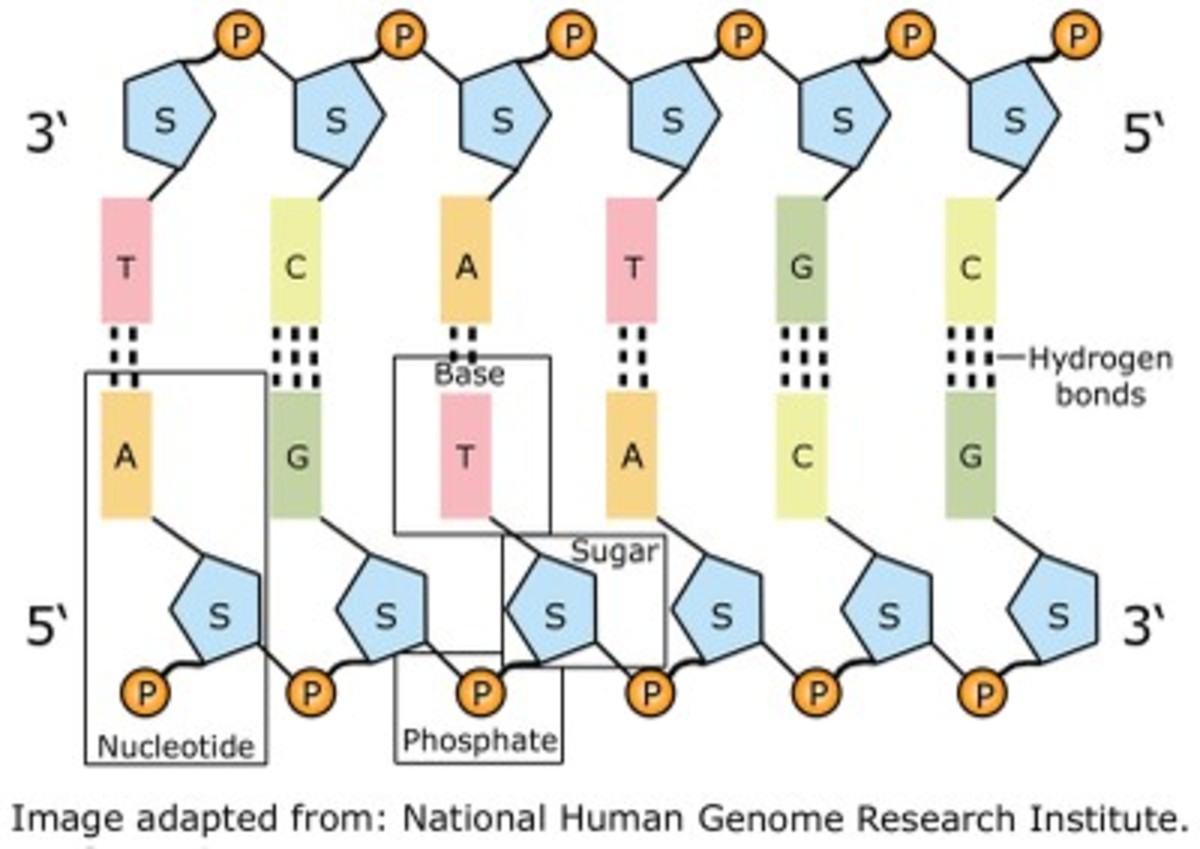
Structure and Function of DNA Microbiology
Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding. Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,. A nucleotide has three parts:. Web recall that dna polymerases incorporate nucleotides (dntps) into a growing strand of dna, based on the..
What is DNA? Nucleotides, Bases and Information Storage HubPages
Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. Web a template strand of dna contains the nucleotide sequence. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand,.
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding. Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. A nucleotide has three parts:. Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,..
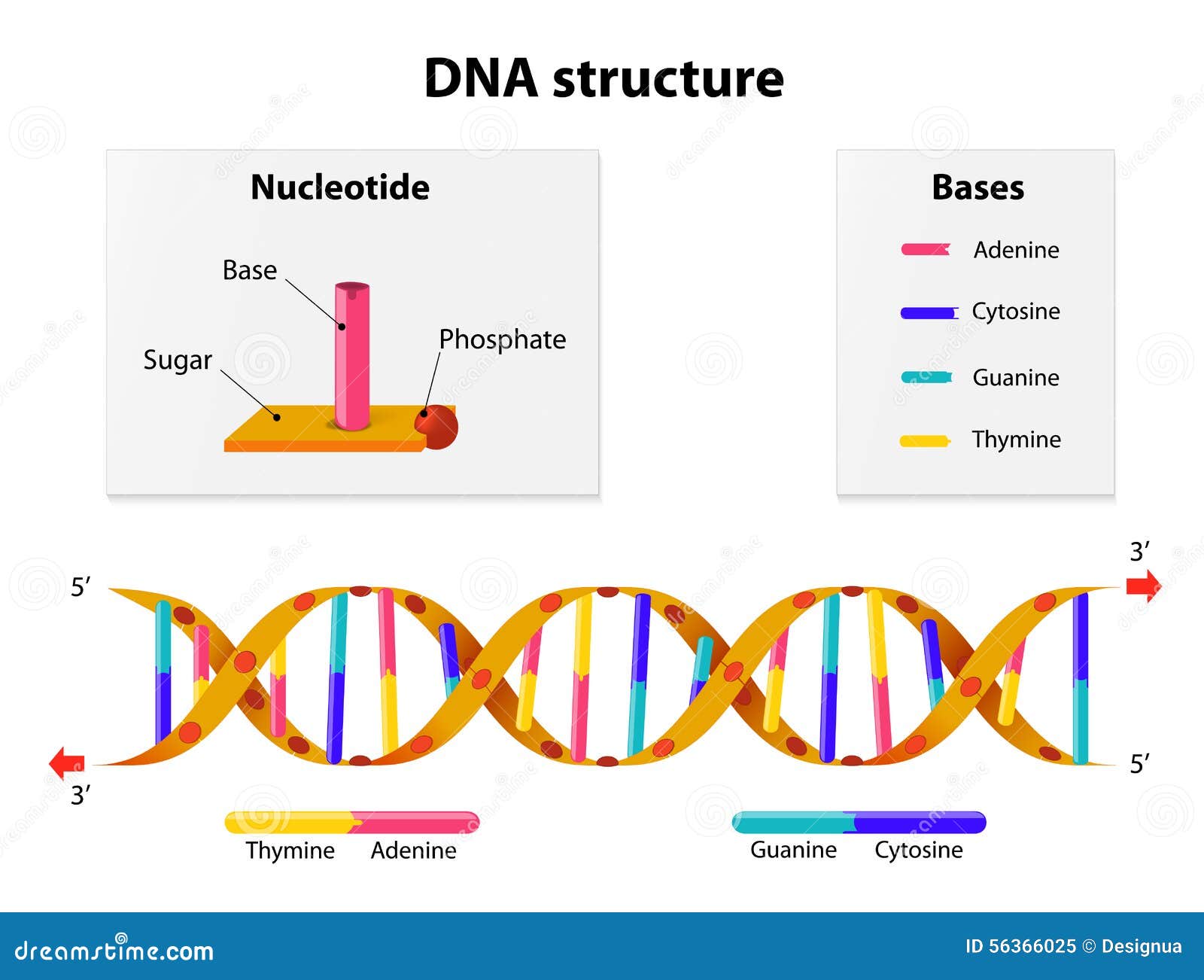
DNA Structure Stock Vector Image 56366025
Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. A nucleotide has three parts:. Web recall that dna.
Structure Of DNA Function, Summary, Diagram & Model
Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,. Web recall that dna polymerases incorporate nucleotides (dntps) into a growing strand of dna, based on the. Web a template strand of dna contains the nucleotide sequence. Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase.
Nucleotides and Bases Generation
Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. Web a template strand of dna contains the nucleotide sequence. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. A nucleotide has three parts:. Web recall that dna polymerases incorporate nucleotides (dntps) into a growing strand.
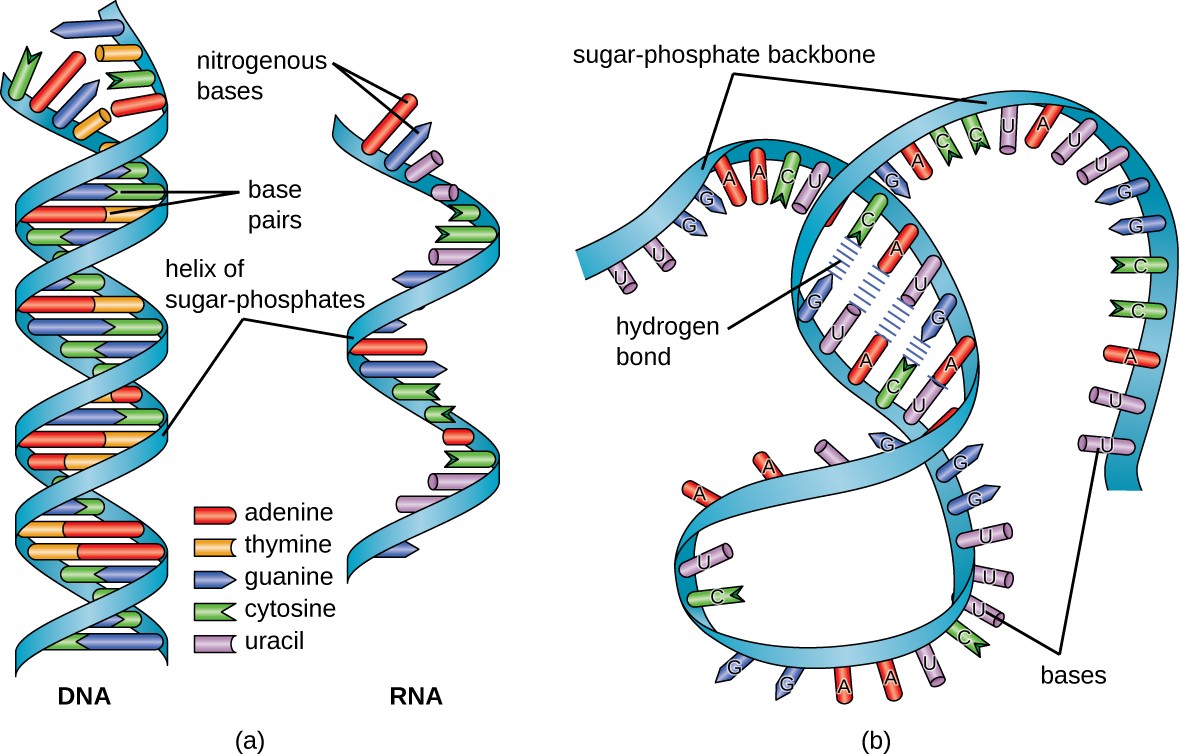
Structure and Function of RNA Microbiology
Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,. Web recall that dna polymerases incorporate nucleotides (dntps) into a growing strand of dna, based on the. Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. Web the building block, or monomer,.
6 Illustration of a nucleotide and a DNA strand. Download Scientific
Web a template strand of dna contains the nucleotide sequence. Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,. Web 5 rows dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved. Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase.
DNA Replication Study Solutions
Web recall that dna polymerases incorporate nucleotides (dntps) into a growing strand of dna, based on the. Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. A nucleotide has three parts:. Web at this point,.
Web 5 Rows Dna Template Strand And The Creation Of Its Complementary Strand The Primary Enzyme Involved.
Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. Web once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding. Web at this point, at least in eukaryotes, the newly synthesized mrna undergoes a process in which noncoding nucleotide sequences,. Web recall that dna polymerases incorporate nucleotides (dntps) into a growing strand of dna, based on the.
A Nucleotide Has Three Parts:.
Web a template strand of dna contains the nucleotide sequence.