Alpha Helix And Beta Pleated Sheet
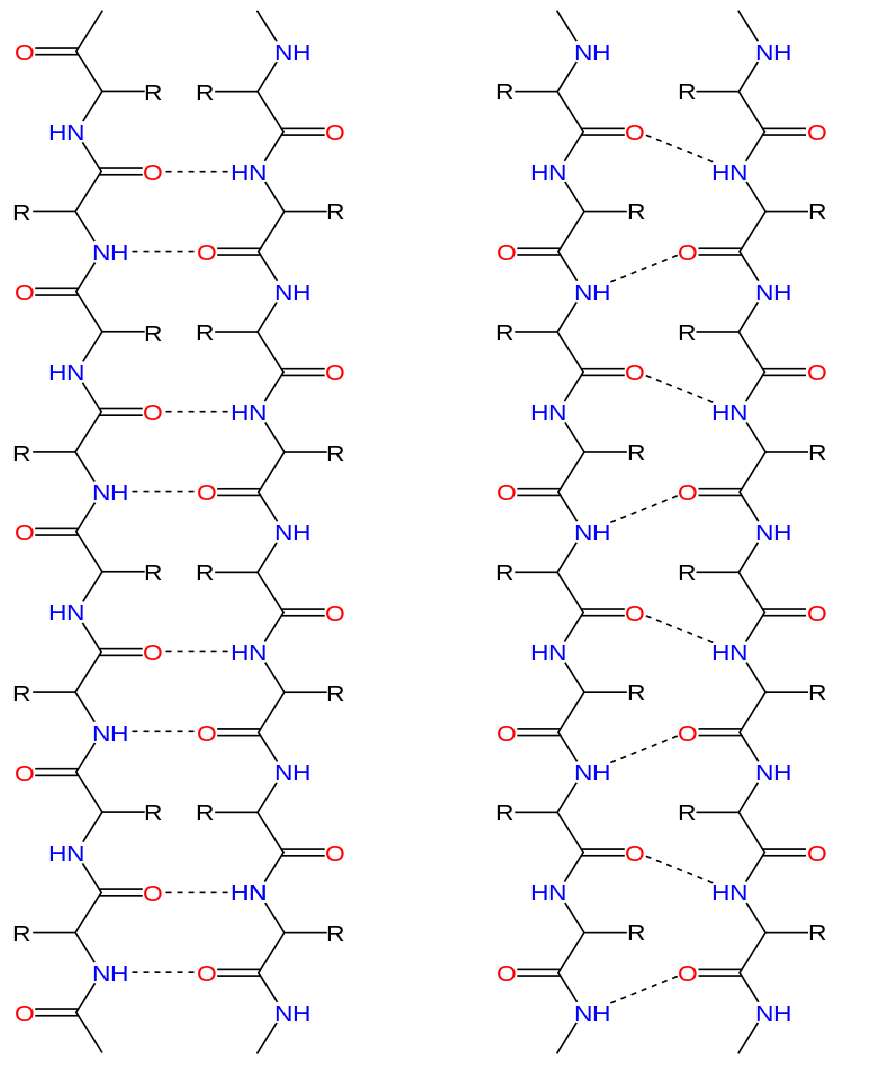
Alpha Helix And Beta Pleated Sheet - Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. The tertiary structure of proteins; This page explains how amino acids combine to make proteins and what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the.
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. The tertiary structure of proteins; Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. This page explains how amino acids combine to make proteins and what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures.
The tertiary structure of proteins; Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. This page explains how amino acids combine to make proteins and what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are.
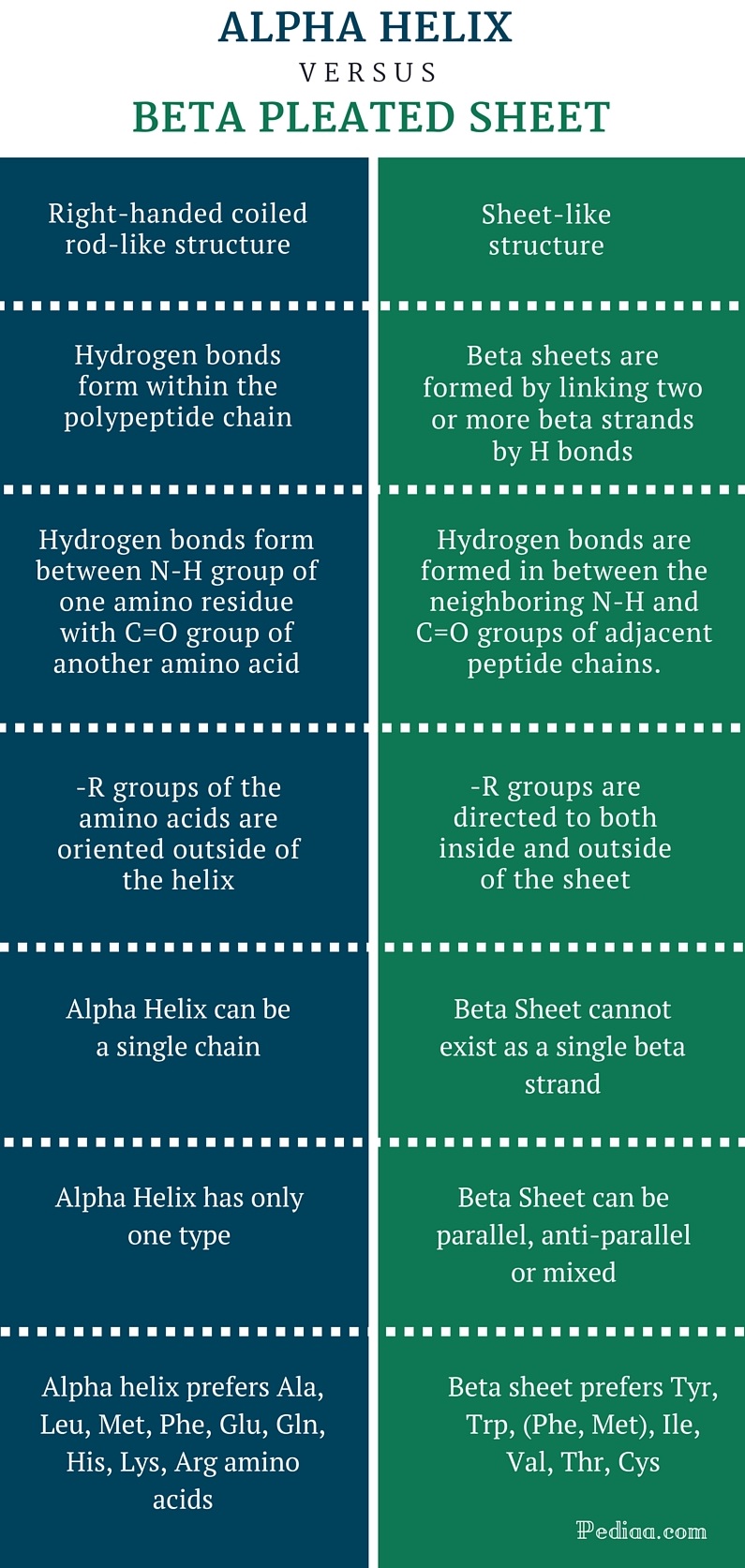
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet
Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This page explains how amino acids combine to make proteins and what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures. The.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet Compare the
The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. The tertiary structure of proteins; Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet
Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. Web the most common.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This page explains how amino acids combine to make proteins and what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino.
College. Science. Life Essential Cell Biology 3rd Ch 4 Protein
The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. This page explains how amino acids combine to.
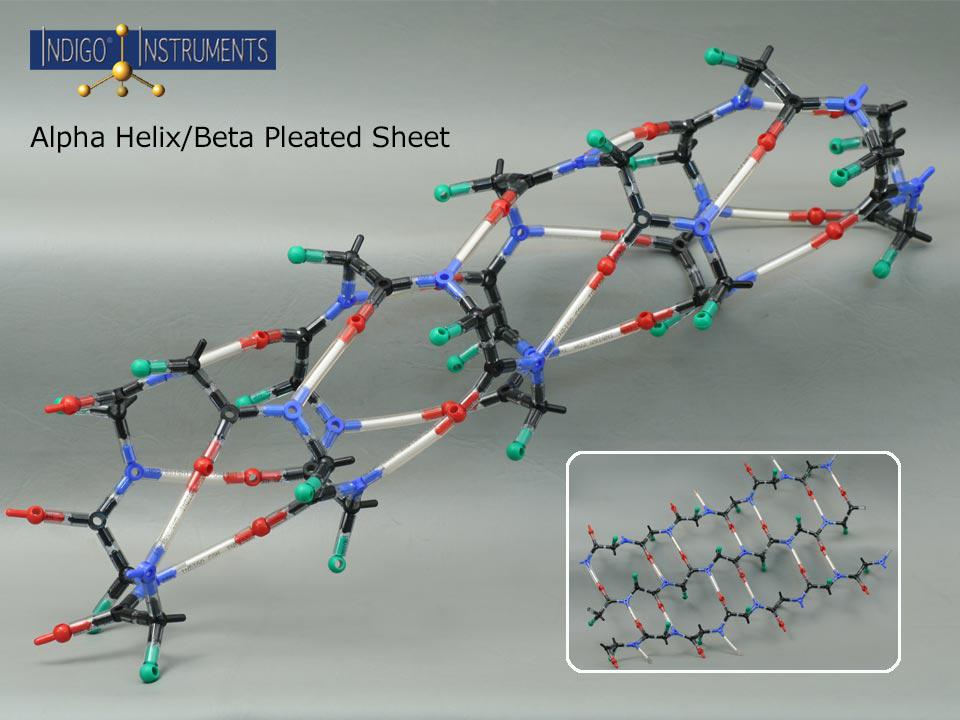
Alpha Helix Structure Molecular Model Kit Complements 12 Base Pair DNA
This page explains how amino acids combine to make proteins and what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino.
Proteins Microbiology
This page explains how amino acids combine to make proteins and what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet Compare the
The tertiary structure of proteins; The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. This page explains.
Secondary structures of keratin protein (beta pleated sheets and alpha
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This page explains how amino acids combine to make proteins and what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino.
[Solved] How many hydrogen bonds involving the backbone CO and NH can
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. The tertiary structure of proteins; Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive.
Web The Most Common Types Of Secondary Structures Are The Α Helix And The Β Pleated Sheet.
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This page explains how amino acids combine to make proteins and what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. The tertiary structure of proteins;






![[Solved] How many hydrogen bonds involving the backbone CO and NH can](https://cdn.testbook.com/images/production/quesImages/qImage646f23abed4806260c7a04d2.png)